【学术前沿】贾大/李国辉/戴伦治团队联合揭示内吞体运输的动态调控机制
内吞体是介导细胞膜表面受体、脂质和信号分子等货物运输的囊泡结构。内吞体上的蛋白能够被转运到溶酶体降解,也能被循环到细胞膜或高尔基体。内吞循环作为细胞活动的基本过程之一,决定了细胞膜上众多蛋白的命运[1-3],从而影响了大量的信号通路,比如葡萄糖的摄取[4]、维持细胞内金属离子的稳定性[5, 6]等。作为一个高度动态的过程,内吞循环也受到包括环境、基因表达、蛋白修饰等诸多因素的调节[5, 7-9]。调节的紊乱和多种神经疾病、糖尿病、免疫性疾病等相关[3]。
自从1998年Scott Emr课题组发现Retromer以来 [10],内吞循环的研究已经取得了巨大的进展。该通路在细胞及生物体整体上的重要性也被多项研究证明。多个重要的调节基因被发现,包括Retromer[10], Retriever[11], WASH复合物[12-14]、SNX(sorting nexin)家族的多个成员[15]、TBC1D5[16, 17]。这些研究揭示了正常情况下内吞体上的蛋白如何被选择性地识别循环,或者降解。但是在应激状态下,细胞为了生存如何动态调控货物的内吞循环很少被探究。
SNX27是内吞循环的一个主要调节蛋白,负责将细胞膜上的蛋白从内吞体循环运输到质膜[5]。SNX27通过其PDZ结构域,与被运输蛋白(货物)C端末尾的PDZ结合基序(PDZbm)相互作用[18]。含有PDZ结合基序的货物包括:葡萄糖转运蛋白GLUT1、轴突导向蛋白SEMA4C,和甲状旁腺激素受体PTHR等[5, 13, 19]。
近日,贾大/李国辉/戴伦治课题组在JCB上发表了题为Phosphorylation of SNX27 by MAPK11/14 Links Cellular Stress Signaling Pathways with Endocytic Recycling的长文。该研究综合利用细胞生物学、生物化学、分子动力学模拟等手段发现了饥饿等刺激抑制部分货物内吞循环的现象,阐释了多种细胞应激通过MAPK11/14对SNX27磷酸化水平的调节作用,证明了SNX27的磷酸化修饰可以动态调节内吞运输的途径。

该研究通过免疫荧光、嵌合体内吞和细胞表面生物素化实验发现饥饿能抑制含PDZ结合基序货物的内吞循环(GLUT1、SEMA4C和PTHR),但对不含PDZ结合基序的货物(TRAILR1)没有影响。
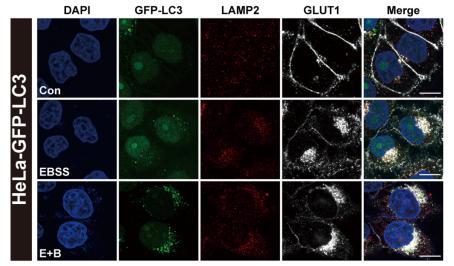
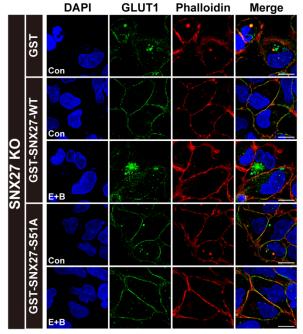
接下来作者排除了TBC1D5 、Retromer复合物、WASH复合物等蛋白在饥饿状态下对内吞循环的调控,并通过质谱、订制特异位点磷酸化抗体证实了饥饿增强SNX27 S51位的磷酸化水平。为了进一步说明饥饿通过SNX27调节货物运输,作者构建了SNX27敲除的细胞系,发现只有回补野生型SNX27能够响应饥饿刺激,导致货物不能正常转运,而回补不能被磷酸化的51A突变体无法响应饥饿刺激,对货物的膜定位没有影响。证明饥饿通过增强SNX27 S51位的磷酸化抑制货物的内吞循环。
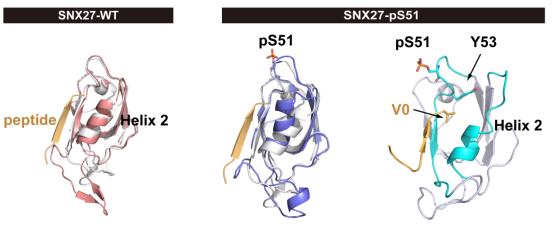
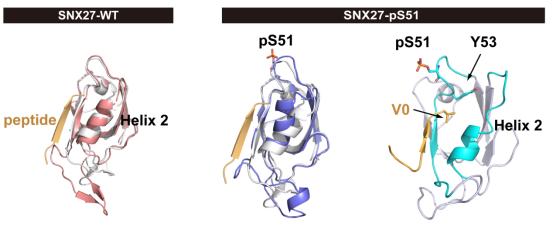
为了阐明磷酸化的SNX27抑制内吞循环的分子机制,作者利用分子动力学模拟发现SNX27 S51位的磷酸化改变了与货物结合口袋的构象,作者进一步通过IP和ITC实验证明了SNX27的磷酸化突变体与含PDZbm货物的亲和力降低。
紧接着,结合生信分析和体外激酶实验找到了SNX27的上游激酶是MAPK通路的MAPK11和MAPK14。发现多种能够激活p38通路的刺激,如LPS、IL-6、EGF和过量的ATP都能增强SNX27的磷酸化,抑制货物的内吞循环。最后,作者提出了多种细胞应激通过激活MAPK11/14增强SNX27 Ser51位的磷酸化水平,降低SNX27与含PDZbm货物的亲和力,从而抑制货物内吞循环的具体模型。
总的来说,作者通过丰富的体内、体外生物学数据阐释了哺乳动物细胞中存在MAPK11/14-SNX27-PDZbm信号通路,揭示了SNX27的磷酸化动态调节内吞循环的分子机制。内吞循环的动态调控能够帮助细胞和生物体适应不断变化的环境条件,为相关疾病的治疗提供了潜在靶点。
据悉,四川大学的博士生毛乐娇和大连化物所廖晨伊为该论文的共同第一作者,四川大学的贾大、戴伦治及大连化物所的李国辉为该论文的共同通讯作者。四川大学的魏于全、孙庆祥、莫显明,华中科技大学的薛宇,梅奥医学中心的Daniel D. Billadeau等为课题提供了大力支持。美国科学院院士、Cornell大学的Scott Emr教授是该论文的Monitoring editor.
参考文献
1. Wang, J., et al., Endosomal receptor trafficking: Retromer and beyond. Traffic, 2018. 19(8): p. 578-590.
2. Burd, C. and P.J. Cullen, Retromer: a master conductor of endosome sorting. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2014. 6(2).
3. Cullen, P.J. and F. Steinberg, To degrade or not to degrade: mechanisms and significance of endocytic recycling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2018. 19(11): p. 679-696.
4. Seaman, M.N., The retromer complex - endosomal protein recycling and beyond. J Cell Sci, 2012. 125(Pt 20): p. 4693-702.
5. Steinberg, F., et al., A global analysis of SNX27-retromer assembly and cargo specificity reveals a function in glucose and metal ion transport. Nat Cell Biol, 2013. 15(5): p. 461-71.
6. Curnock, R. and P.J. Cullen, Mammalian copper homeostasis requires retromer-dependent recycling of the high-affinity copper transporter 1. J Cell Sci, 2020. 133(16).
7. Nooh, M.M. and S.W. Bahouth, Two barcodes encoded by the type-1 PDZ and by phospho-Ser(312) regulate retromer/WASH-mediated sorting of the ss1-adrenergic receptor from endosomes to the plasma membrane. Cell Signal, 2017. 29: p. 192-208.
8. Kimura, N., et al., Dynein Dysfunction Reproduces Age-Dependent Retromer Deficiency: Concomitant Disruption of Retrograde Trafficking Is Required for Alteration in beta-Amyloid Precursor Protein Metabolism. Am J Pathol, 2016. 186(7): p. 1952-1966.
9. Yao, J., et al., Mechanism of inhibition of retromer transport by the bacterial effector RidL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018. 115(7): p. E1446-E1454.
10. Seaman, M.N., J.M. McCaffery, and S.D. Emr, A membrane coat complex essential for endosome-to-Golgi retrograde transport in yeast. J Cell Biol, 1998. 142(3): p. 665-81.
11. McNally, K.E., et al., Retriever is a multiprotein complex for retromer-independent endosomal cargo recycling. Nat Cell Biol, 2017. 19(10): p. 1214-1225.
12. Gomez, T.S. and D.D. Billadeau, A FAM21-containing WASH complex regulates retromer-dependent sorting. Dev Cell, 2009. 17(5): p. 699-711.
13. McGarvey, J.C., et al., Actin-Sorting Nexin 27 (SNX27)-Retromer Complex Mediates Rapid Parathyroid Hormone Receptor Recycling. J Biol Chem, 2016. 291(21): p. 10986-1002.
14. Jia, D., et al., WASH and WAVE actin regulators of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) family are controlled by analogous structurally related complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010. 107(23): p. 10442-7.
15. Gallon, M. and P.J. Cullen, Retromer and sorting nexins in endosomal sorting. Biochem Soc Trans, 2015. 43(1): p. 33-47.
16. Seaman, M.N., et al., Membrane recruitment of the cargo-selective retromer subcomplex is catalysed by the small GTPase Rab7 and inhibited by the Rab-GAP TBC1D5. J Cell Sci, 2009. 122(Pt 14): p. 2371-82.
17. Jia, D., et al., Structural and mechanistic insights into regulation of the retromer coat by TBC1d5. Nat Commun, 2016. 7: p. 13305.
18. Gallon, M., et al., A unique PDZ domain and arrestin-like fold interaction reveals mechanistic details of endocytic recycling by SNX27-retromer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2014. 111(35): p. E3604-13.
19. Chan, A.S., et al., Sorting nexin 27 couples PTHR trafficking to retromer for signal regulation in osteoblasts during bone growth. Mol Biol Cell, 2016. 27(8): p. 1367-82.
原标题:《【学术前沿】贾大/李国辉/戴伦治团队联合揭示内吞体运输的动态调控机制》

